Recession Remedies Home
Abstract
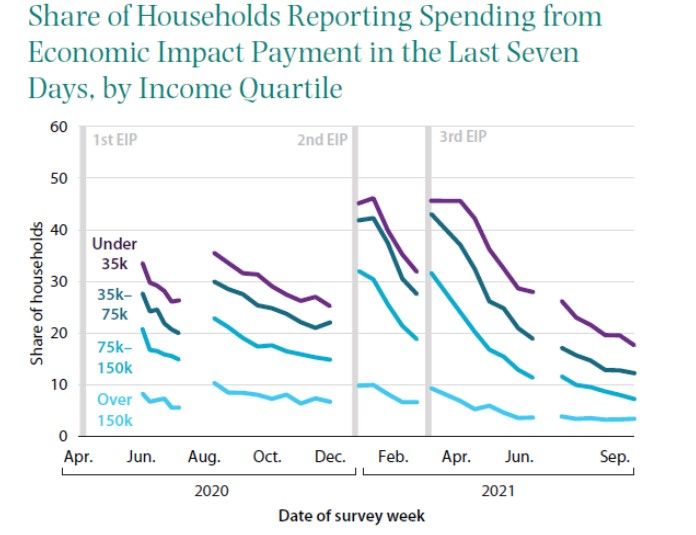
The authors examine the more than $800 billion in cash that was distributed to all but the highest-income households in the three rounds of Economic Impact Payments (EIPs). Although there were delays in getting the money to some vulnerable, low-income households, electronic disbursement allowed the Treasury to make payments quickly—about two weeks after the initial legislation was signed and even more quickly in the subsequent rounds. The available evidence suggests that the payments led to a rapid increase in spending; consumers spent about the same or a smaller fraction of these payments relative to similar payments in past downturns. The payments were not, of course, well targeted. Some households that weren’t adversely affected by the pandemic received the money, but other recipients were adversely affected but weren’t eligible for or didn’t promptly receive more targeted benefits (such as UI or rental assistance) and were greatly aided by the EIPs.